face without opening flameproof
enclosures.
Intelligent software
modules
Caterpillar distinguishes between
different levels of shearer automation,
from basic to advanced.
Each of the company’s shearers is
equipped with a basic automation
package. This package allows the
machine to be operated by remote
control and to switch all equipment
safely while monitoring the operation.
This package also includes some
automation logic that can reduce
overload situations, as well as some
diagnostic tools for troubleshooting
and problem‑solving.
Alternatively, Caterpillar offers two
more complex automation packages:
automation control and advanced
automation control.
Automation control includes
important features, such as extended
gate end communication, which
provides data exchange with other
longwall components. This automation
level allows the ranging arms to be
operated in a high‑quality closed‑loop
operation for precise steering. It also
provides a collision avoidance function
to prevent collision between the
shearer and the shields operated by a
Cat PMC‑R.
The most important feature is
state-based automation (SBA). SBA
allows definition of the full cutting
cycle of the machine along the face for
both cutting directions between
maingate and tailgate, as well as the
cleanup operation at the gate ends. It is
important to specify automation
parameters, including cutting height,
speed and cutting mode, all of which
can be defined in as many as 40
different zones along the face. This is
called zone‑based automation.
Caterpillar has created several
preset cutting modes that can be
chosen in each automation state.
The advanced automation control
package includes a feature called
LongwallNavigator, which combines
Caterpillar software tools in the gate
ends and in the shield controllers into
one package that offers advanced
geometry and trigonometry
calculations for full 3D navigation, as
well as an advanced floor profile
calculation and a high level of sensor
technology.
These technologies make it possible
to achieve horizon control, extraction
control and race alignment. Extraction
control allows the machine to follow
defined floor and roof profiles along
the face, following any given coal seam
undulations for optimal extraction and
production. At the same time, horizon
control guides the machine to follow
the seam undulations in the direction
of the machine’s advance. Face
alignment keeps the face straight for
consistent production and minimal
wear of the conveyor system.
All these automation features
support both uni‑directional and
bi‑directional mining methods.
Caterpillar can also support additional
customer-specific automation
processes, including complex longwall
top coal caving (LTCC) operation in
combination with fully‑automated roof
supports. In this case, the PMC Evo‑S
control system provides continuous
information to the PMC‑R roof support
controls to steer the face conveyor
push operation.
SBA is an efficient tool for defining
and controlling complex automation
cycles. It allows the shearer to operate
precisely according to the operator’s
defined production process, including
directions, speeds, arm heights, cowl
positions and ranging arm control
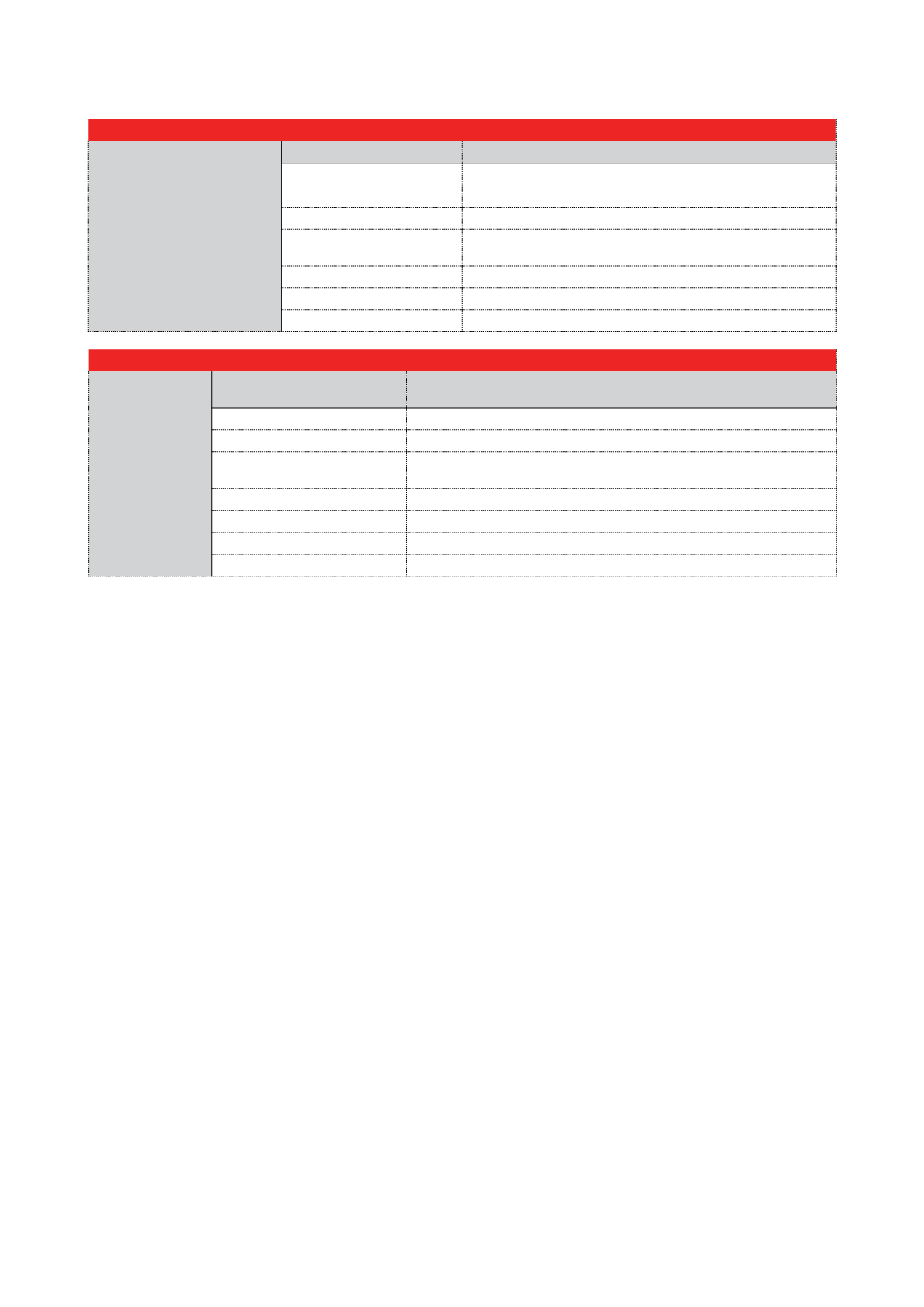
Table 1. Basic control functions of a longwall shearer
Basic control
Manual operation
Provide manual operation: only PLC
Shearer radio control software Allow miner to operate the shearer via radio control
Standard display
Provide the visualisation of the operation related values and parameters
Self monitoring
Permanently check all operation related components and functions
Safety functions
Tilt sensor monitoring in radio handheld, monitoring of the radio
connection, etc.
Speed limiting
Definition of up to 10 speed zones along the face
Display/HMI tools
For miner-machine interaction
Cutter motor feedback
Controlled breaking of haulage speed depending on cutter load
Table 2. Automation Control: the next level of automation functions for a longwall shearer
Automation control
Basic control +
Advanced automation of low accuracy using inclinometers: PLC and IPC (accuracy
< 100 mm along the machine length)
Gate end communication
Provide data exchange with other longwall components
Collision avoidance
Prevention of collision between shearer and shields
State-based automation (including
zone-based parameters)
Definition of automation parameter in zones along face: up to 40 different zones
Ranging arm closed-loop control
For exact ranging arm position control
Cutting modes
Allows to operate the shearer via radio control
Common automation features
Cutter motor feedback, etc.
Onboard system diagnostics
For easy troubleshooting
52
|
World Coal
|
August 2015


