surface moisture; however, use of
flocculant to pre-treat the filter feed
yields increases in filter throughput.
Use of steam addition, to supplement
the filtration process, significantly
increases the filter throughput and
reduces the final product surface
moisture by between 5% and 10%
(absolute) relative to the corresponding
air only case.
The process air duty to achieve a
baseline surface moisture increases as
the filter feed particle size distribution
becomes finer. For example, with an air
usage of 50 Normal (N) m
3
/t, the
Queensland metallurgical coal with a
P
50
of 0.10 mm will achieve a surface
moisture of 15%. The considerably finer
New Zealand metallurgical coal with a
P
50
of 0.02 mm will achieve a surface
moisture of 20% with the same air
usage.
The final moisture outcomes at the
high pressure settings were consistent
with the QCAT testing results.
New Zealand metallurgical
coal study
This study was managed by Brightwater
Engineering Limited (BEL) and QCC
provided engineering services to
develop the design of the proposed new
flotation facility. The proposed upgrade
aimed to process the combined -0.2 mm
streams from the existing 320 tph (ar)
coal preparation plant (CPP). A tailings
reclaim operation would also supply
fines to the existing plant, and this was
allowed for in the design. The nominal
design capacity of the proposed flotation
facility was 96 tph (ad) of fresh feed.
The process design and plant layout
developed as part of the study included:
n
Three 70 m
3
froth flotation tank cells
in a series (cell to cell) configuration.
n
One 20 m dia. coal thickener.
n
One x 70 m
2
hyperbaric disc filter
and process air compressor.
n
Diesel-fired boiler and boiler water
feed treatment plant.
n
Ancillary services.
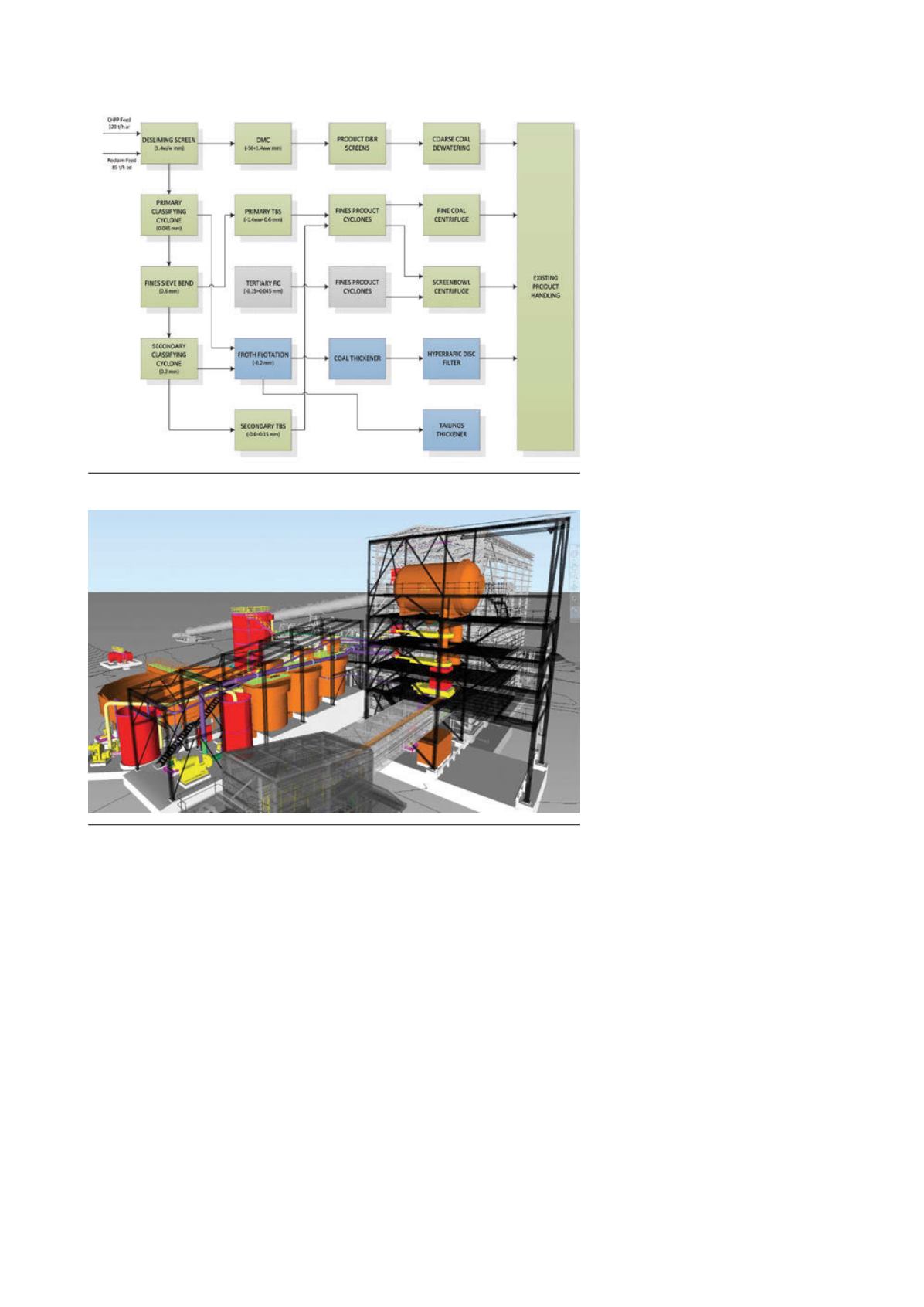
The plant process flowsheet and a 3D
Navisworks view of the proposed
facility are provided in Figures 5 and 6.
Projected plant production and yield
increases were developed for all feed
types for normal operating conditions.
For a hyperbaric filter with steam
addition, a filtercake total moisture of
approximately 10% was guaranteed by
the OEM. For the nominal design case,
this will result in a production increase
of approximately 51 tph (ad) and an
overall plant yield increase of 3.8% (ar),
and a negligible (0.1%) increase in
overall washed coal moisture.
The hyperbaric disc filter would
require 90 Nm
3
/t (or 4100 Nm
3
/hr) of
process air with a delivery pressure of
0.6 MPa and 80 kg/t of process steam, to
achieve the target filtercake total product
moisture of 10% (ar).
The estimated total operating costs
(2012 basis) for the proposed plant is
projected to be NZ$16.33 t of flotation
feed. The boiler diesel consumption
would constitute approximately 50% of
this operating cost.
This project is currently on hold due
to the poor prevailing market conditions
for hard coking coal.
New South Wales thermal
coal flotation upgrade
study
This study was managed by QCC to
develop the design of the proposed
flotation facility to feasibility level.
The proposed upgrade aimed to
process the primary classifying cyclone
overflow (-0.09 mm) and the fines
product screen underflow (-0.25 mm).
Figure 5. New Zealand metallurgical coal flotation upgrade – flowsheet.
Figure 6. New Zealand metallurgical coal flotation upgrade study.
72
|
World Coal
|
June 2015


